Introduction To Gender Discrimination
Despite the significant advancements made in the direction of gender equality, gender discrimination continues to be a problem that affects societies all over the world. In this blog, we'll look at the various manifestations of gender discrimination, where it comes from, and how it affects both people and society as a whole. Our goal is to spread knowledge and promote a better understanding of this pervasive issue.
Why and How this spreads
The prevalence or rise of gender discrimination in society is a complex issue that has persisted for many years. It's important to look at a number of contributing factors in order to understand why and how gender discrimination has gotten worse in our society. Remember that these variables can change depending on the area and the situation, but some typical trends include:
1) Gender Equality Movements
Sometimes, progress made by movements for gender equality can result in an increase in gender discrimination. When initiatives to question conventional gender roles and advance equality gain traction, there might be a backlash from people or groups that are opposed to change. Little bit details of Gender Equality movements are listed Below:
1st Period of Feminism (Late 19th and Early 20th Century):
Women's suffrage and legal rights, such as property ownership and marriage rights, were the main topics of this wave of feminism. Emmeline Pankhurst in the United Kingdom and Susan B. Anthony and Elizabeth Cady Stanton in the United States played important roles in this movement.
 |
| First Wave of Feminism |
2nd Period of Feminism (1960s and 1970s):
This wave of feminism broadened its focus to include a variety of issues, such as domestic violence, workplace discrimination, and reproductive rights. Bell hooks, Gloria Steinem, and Betty Friedan were among the influential activists.
 |
| Second Wave of Feminism |
3rd Period of Feminism (1990s and Beyond):
In order to address intersectionality, the third wave of feminism takes into account the distinctive experiences of women of colour, LGBTQ+ people, and people with disabilities. It casts doubt on the idea of a uniform "women's experience" and places a strong emphasis on personal autonomy and decision-making.
 |
| Third Wave of Feminism |
Transgender and LGBTQ+ Movements:
These movements have prioritised advancing the acceptance and rights of transgender and gender nonconforming people. Famous activists like Marsha P. Johnson and Sylvia Rivera were instrumental in the early LGBTQ+ rights movement, and activists today still fight for equality and safety.
 |
| LGBTQ+ Right Movement |
#MeToo Movement:
The #MeToo movement, which emerged in the twenty-first century, has brought attention to sexual harassment and assault issues. It has given survivors the confidence to tell their stories, confront the offenders, and spread awareness of how widespread these problems are.
 |
| #MeToo Movement |
Global Women's Movements:
Not only Western nations are experiencing gender movements. Women's movements have played a significant role in promoting women's rights around the world, combating gender-based violence, and encouraging economic and educational opportunities for women in various parts of the world.
 |
| Protest for Women Rights |
Intersectional Feminism:
The emphasis on intersectionality in many modern gender movements recognises the interconnectedness of various forms of oppression, including racism, sexism, and classism. The goal of intersectional feminism is to address these related issues and offer a more open-minded and just framework.
 |
| Picture from Intersectional Feminism Movement |
Policy and Legal Changes:
2) Political Leadership
Governments and political leaders attitudes and policies can have a big impact. In some instances, the emergence of political figures with conservative views on gender roles can result in the implementation of discriminatory or backward-looking laws.
Of course, the following information focuses on political figures and how they may address or support gender discrimination:
Political Leaders Contributing to Gender Discrimination:
Viktor Orban (Hungary): Orban, the country's prime minister, has drawn flak for taking a traditionalist stance on gender issues. He has come under fire for supporting traditional gender roles and values after his government passed laws restricting the rights of transgender and intersex people.
 |
| Viktor Orban |
Turkey's Recep Tayyip Erdoan: The Turkish president has been accused of undermining gender equality in the nation. Widespread criticism has been levelled at his government's decision to leave the Istanbul Convention, an international agreement to end violence against women.
.jpg/1200px-President_Recep_Tayyip_Erdo%C4%9Fan_1_(cropped_2).jpg) |
| Recep Tayyip Erdogan |
Jair Bolsonaro (Brazil): Human rights organisations are alarmed by the Brazilian president's controversial remarks about women and LGBTQ+ people. His rhetoric has drawn criticism for encouraging an atmosphere that is hostile to people who identify as gender and sexual minorities.
 |
| Jair Bolsonaro |
Political Leaders Challenging Gender Discrimination:
Jacinda Ardern (New Zealand): Ardern, the country's prime minister, is renowned for taking a proactive approach to gender-related issues. She put into effect measures such as the "Wellbeing Budget," which emphasises social indicators like domestic violence and mental health. She has also been a strong supporter of women's rights and equal pay.
 |
| Jacinda Ardern |
Angela Merkel (Germany): As Germany's first female chancellor, Angela Merkel is well-known in the political world of Europe. She has been a steadfast supporter of women holding leadership positions and workplace equality. Women now hold more prominent positions in German politics and society thanks to her leadership.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/GettyImages-1052170818-c74dbcfa3e474aa89bb897a14f0dbe32.jpg) |
| Angela Merkel |
Justin Trudeau (Canada): The country's prime minister has actively supported gender equality and worked to advance women's rights both domestically and internationally. He has appointed a gender-balanced cabinet and started programmes to combat discrimination and violence against women in Canada.
 |
| Justin Trudeau |
Political Movements and Gender Discrimination:
Women's Rights Movements: Organisations and movements that support gender equality for women frequently put pressure on political leaders. These movements may have an impact on laws governing representation in government, reproductive rights, and equal pay.
 |
| Women Movements |
Conservative and Populist Movements: Movements that are sceptical of efforts to advance gender equality include conservative and populist political movements in some cases. These movements might aim to reverse gender-related progressive policies, igniting discussions and conflicts about women's and LGBTQ+ rights.
 |
| Populist Movements for LGBTQ+ rights |
Intersectionality and Global Movements: Economic inequality and racism are two forms of discrimination that are frequently linked to gender discrimination. Political figures and movements that place a high priority on intersectionality address the interconnectedness of these problems and look for all-encompassing answers to the discrimination problem.
3) Social Media
The internet and social media platforms have given people a platform to voice their opinions, which can either advance gender equality or encourage harmful actions like cyberbullying, harassment, and the dissemination of sexist or misogynistic material.
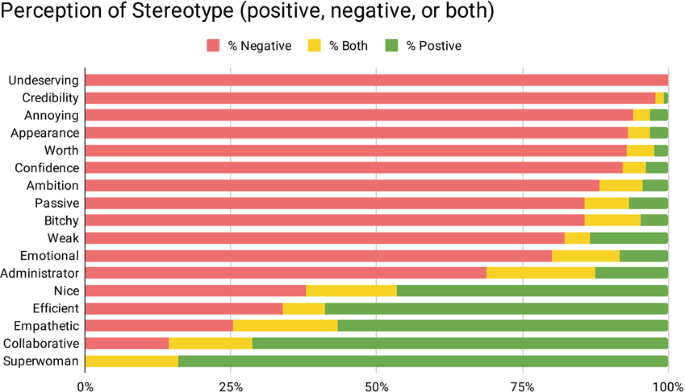
Stereotypes and damaging narratives are amplified:
Social media sites can both contribute to and amplify gender inequality. On these platforms, negative stereotypes and stories that support gender bias are frequently amplified. Memes, jokes, and offensive content can spread quickly and reinforce negative stereotypes of gender roles and expectations.
Body-shaming, objectification of women, and the spread of sexist jokes and memes, for instance, can normalise and maintain negative gender stereotypes. Such material can have a particularly negative impact on people's mental and emotional well-being and can foster a discriminatory culture.
 |
| Perception of Stereotype |
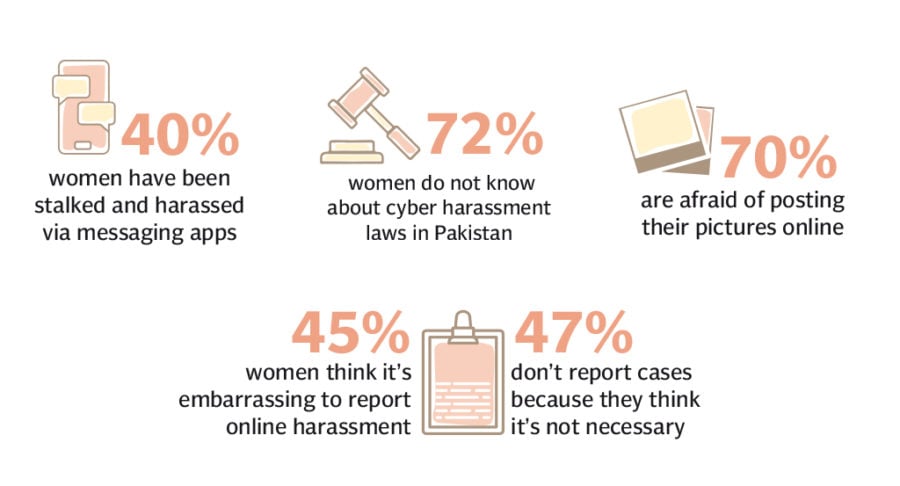
Online Harassment and Cyberbullying:
On social media sites, cyberbullying and harassment based on gender are pervasive. Online abuse, such as threats, sexual harassment, and the sharing of personal information, often targets women and people of colour disproportionately. People may be discouraged from taking part in online discussions or expressing their opinions due to this hostile online environment.
Although different social media platforms take different approaches to combating online harassment, the problem still exists. These platforms have become a breeding ground for gender-based violence and discrimination due to their anonymity and ease of spreading hate.
 |
| Online Harrasement Report |
Activism and Empowerment:
Social media can be a powerful tool for empowerment and activism, even though it can also be a source of gender discrimination. Social media's reach and connectivity have been leveraged by movements like #MeToo and #YesAllWomen to increase public awareness of gender-based violence, sexual harassment, and other related issues.
Individuals can connect with like-minded activists on social media platforms, share their experiences, and organise for change. They have played a crucial role in holding people and organisations responsible for gender-based discrimination and giving previously silenced voices a platform.
 |
| Gender Activist Movements |
4) Education + Awareness
Lack of knowledge and awareness of issues pertaining to gender equality may also be correlated with an increase in gender discrimination. Injurious beliefs and behaviours can persist if the effects of discrimination are not sufficiently understood.
Gender Discrimination and Access to Quality Education:
The persistence or eradication of gender discrimination depends critically on access to high-quality education. Girls and women still encounter significant obstacles to education in many parts of the world, such as cultural norms, poverty, and a lack of secure and accessible schools. By limiting girls' life options and economic opportunities, denying them educational opportunities contributes to the perpetuation of gender discrimination.
Key Ideas:
Lower enrollment rates for girls in some areas are one aspect of gender disparities in education.
Girls' access to education is hampered by discriminatory practises like early marriage or restrictions on female mobility.
Gender bias in educational systems can be exacerbated by a lack of female teachers and gender-responsive curricula.
Stereotyping and Gender Bias in Educational Content:
By using stereotypical teaching methods and biassed curricula, educational systems can reinforce gender discrimination. Textbooks and other educational materials may perpetuate stereotypes and traditional gender roles that show men as the breadwinners and women as the homemakers. This restricts career options and strengthens societal norms that can breed discrimination in a variety of spheres of life.
Key Ideas
Girl students' aspirations in STEM fields and leadership positions may be hampered by curricula that reinforce stereotypes.
A distorted understanding of women's historical and contemporary contributions can result from gender bias in textbooks.
Stereotyping can affect opportunities and outcomes by influencing teachers' and students' expectations of and attitudes towards one another.
Education for Empowerment:
Education has the potential to be an effective weapon in the fight against gender inequality. Girls and women can become more powerful in economic, social, and political spheres when they have access to high-quality education. Individuals can challenge gender norms and stereotypes, take part in decision-making, and escape the cycle of discrimination with the aid of education.
Key Ideas
Women who have received education typically have better economic prospects and contribute to the welfare of their families and communities.
Education can encourage critical thinking and awareness, which can assist people in identifying and opposing gender discrimination.
Initiatives for gender-inclusive education seek to develop settings that support diversity and gender equality.
 |
| Education Promoting Gender Discrimination |
Negative and Positive Impacts on Individuals and Society
Though the negative effects are more common and significant, gender discrimination has wide-ranging effects on people and society. It can manifest in both positive and negative ways. The following are some effects of gender discrimination, both good and bad:
1) Negative Impacts of Gender Descrimination
Every issue has some postive and negative impacts:
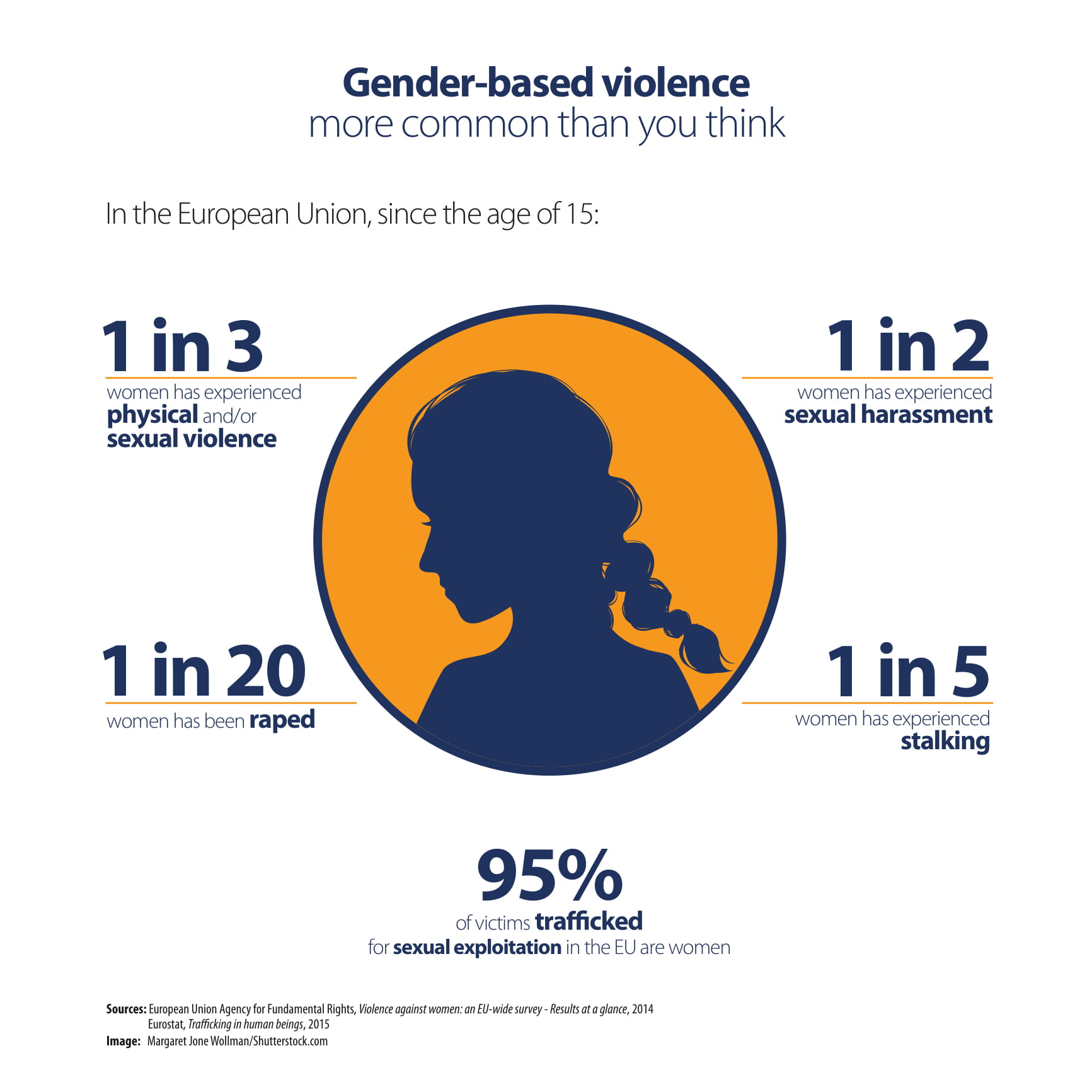
Violence and Harassment:
Gender-based violence, such as domestic abuse, sexual harassment, and human trafficking, can result from gender discrimination. These types of violence have serious emotional and physical repercussions.
 |
| Analysis of Women Harassment |
Psychological:
Discrimination can cause stress and emotional strain that can have a long-term negative impact on mental health. Whether overt or covert, discrimination can cause anxiety, depression, and low self-esteem.
2) Postive Impacts
Postive Impacts of this issue are:
Policy Reforms
Governments and organisations may enact policies and laws aimed at reducing gender discrimination and promoting equality in response to public pressure and advocacy.
Awareness and activism:
Discrimination experiences can spur people to speak out and support gender equality in their communities and among themselves. The deconstruction of discriminatory systems and positive changes are both possible outcomes of this activism.
 |
| Image from Protest for Gender Equality |


Comments
Post a Comment